- 16th Apr, 2025
- Esophageal Dilatation
Esophageal Strictures: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Do you often feel something is stuck in your throat? Or is there a kind of choking sensation even though you have swallowed? Well, this mainly happens when the esophagus gets narrowed or constricted. The condition is known as esophageal stricture.
The esophagus is a tube that runs from the mouth to the stomach and is responsible for carrying food. Now, strictures develop when a channel in the body gets constricted or blocked. Whenever any individual suffers from esophageal stricture, he finds it hard to swallow solids and liquids.
Esophageal strictures are a serious condition and must be treated immediately; otherwise, it might worsen over time and eventually prove to be fatal. One of the effective methods is esophageal dilatation, which aims to widen the esophagus.
Let’s discuss its symptoms, causes and effective treatment options for managing the condition.
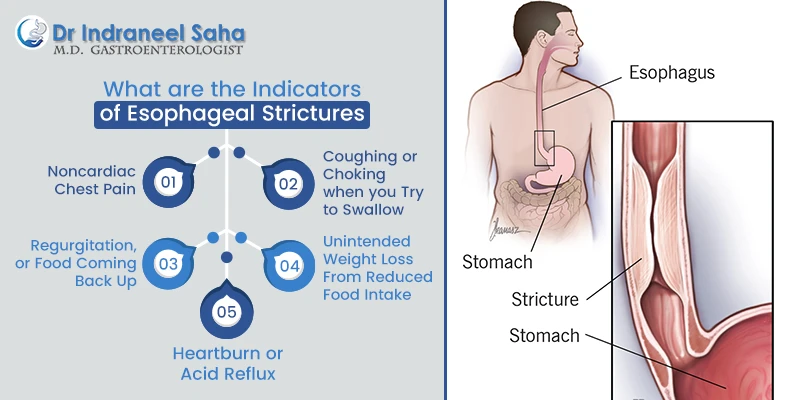
Indicators of Esophageal Strictures
The first and foremost symptom of esophageal strictures is difficulty in swallowing. For the time being, you can manage the condition by taking smaller bites; however, as the disease progresses, these adjustments might not help that much. Here are the other symptoms which patients most likely experience.
- Noncardiac chest pain
- Coughing or choking when you try to swallow.
- Regurgitation, or food coming back up.
- Unintended weight loss from reduced food intake.
- Heartburn or acid reflux
If you are experiencing these symptoms for quite a long time, please consult your healthcare provider today to find out the exact cause of these issues.
Causes of Esophageal Strictures
Many different diseases cause esophageal strictures. They can be either inside or outside the esophagus. If the disorder is related to the inside of the esophagus, it causes the wall of the esophagus to swell up so that it no longer stretches whenever patients swallow food.
On the other hand, narrowing from outside the esophagus occurs due to pressure from the nearby organs and growths.
Some of the Common Causes include the following:
GERD: This is one of the most common causes of esophageal strictures. Constant throwing up of the stomach’s acidic content in the esophagus irritates and damages the esophageal lining. As a result, there is inflammation and scarring, which leads to narrowing over time.
Esophageal injury: Injuries from corrosive substances or medical treatments like radiation therapy result in stricture formation.
Tumours: Abnormal growth near the esophagus causes its narrowing as they press against the esophageal wall.
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: It is an allergic reaction that leads to inflammation in the esophagus and the formation of strictures.
Injury: Injury to the esophagus from endoscopy and surgical intervention results in scarring and strictures.
Treatment of Esophageal Strictures
Diagnosis of esophageal strictures is usually done by a gastroenterologist. You will be asked about your symptoms and medical history. Your healthcare provider will also suggest imaging tests to look for evidence of the strictures, based on which the treatment plan will be prepared.
Here are some of the common approaches.
Esophageal dilatation: It is one of the safe and effective procedures to treat esophageal strictures. It is an outpatient procedure that involves stretching the esophageal muscles to make swallowing easier. During esophageal dilatation, a balloon is inserted into the esophagus through the endoscope to stretch the constricted area. Once it is stretched to the desired width, the balloon is removed.
Medications: Sometimes, doctors prescribe steroid injections at the site of the stricture to reduce inflammation of the esophagus. This is useful in mild cases.
Surgery: If the patient becomes unresponsive to treatment or if the stricture turns malignant, surgery is the only option to remove all or part of the esophagus.
Conclusion
If you notice any issues in the esophagus, seek early treatment rather than keeping the condition as it is. It will prevent the formation of strictures and help you lead a healthy life.